Cannabinoids and their receptors are in nature present throughout the entire human body and because of this, scientists believe that the compounds provides various physiological functions which is mostly true in the brain as well as in the spinal cord, which hold numerous CB1 receptors. What happens is that when cannabinoids unite to these receptors, they start a chain reaction that slows down the diffusion of nerve impulses between cells. This is not always what happens in other nerve cells, though. CB1 receptors are ordered in such a manner that they hasten the release of messages along the neural pathways.
CB1 receptors are largely found in parts of the brain that control memory, movement, complex thought, and response to stress which are functions that are surprisingly not affected by marijuana. Researches show that the body’s natural cannabinoids play an innate role in all of the processes involved including and the control of nausea, vomiting, and pain perception.
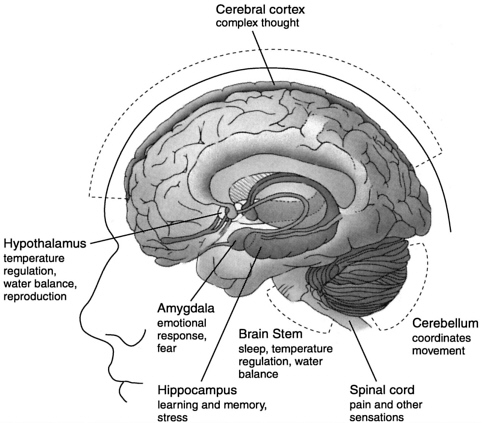
It has been observed that under the influence of marijuana, people’s bodies tend to be affected and they often have a hard time holding their hands steady. In conducted laboratory experiments, it was found out has shown to restrain their activity. Since CB1 receptors are concentrated mostly in regions of the brain that are responsible for movement coordination, it is probable that these receptors account for the various effects of cannabinoids on activity and movement.
Because cannabinoids influence movement through different routes, they encourage a great probable source of new medicines that could treat movement disorders. Moreover, CB1 receptors are reasonably plentiful in areas of the spinal cord and brain controlling pain perception. In laboratory experiment that are designed to measure animals’ responses to escapable and moderate pain, animals responded almost the same to those that were given pain-killing opiate drugs like morphine.
Aside from that, cannabinoids also seem to play a role in pain transmission down peripheral nerves that are responsible in detecting sensations in the entire human body and relay messages to the brain through the spinal cord. These peripheral nerves exhibit both CB1 and CB2 receptors on their surfaces and studies in animals under experimentation indicate that cannabinoids exact to every receptor type are able to block nerve pain. The results imply that a fusion of cannabinoids could actually enhance each other’s effect in alleviating peripheral pains in humans.
A lot of people have claimed to have found release from medical symptoms of nausea and vomiting by ingesting or smoking marijuana. Clinical studies show that both smoked marijuana and THC has the ability to reduce vomiting to a certain extent; researchers have discovered cannabinoid receptors in relatively great quantity in the region of the brain that controls visceral sensations which include vomiting and nausea.
Mack, Alison, Joy, Janet. “Front Matter.” Marijuana As Medicine?: The Science Beyond the Controversy. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2000.
